**This is an old revision of the document!**
Table of Contents
Calculations
Overview
Keyboard Maestro supports calculations in almost any numeric text fields. For example you can Pause for “60*Time in Minutes”. Calculations can also use comma separated lists of numbers as arrays, and can return such arrays, so you can operate on frames and points. Numeric fields often start small with up/down step arrows, but if you type anything other than a number they will expand to allow a more complex expression to be entered. You can tell that a field accepts calculations because a small C shows in the field while editing it.
Examples
For example:
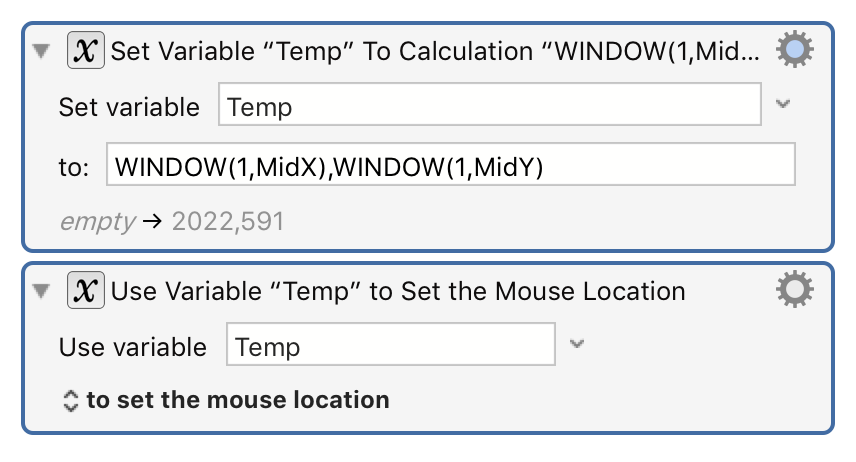
will result in the mouse being placed at the center of the front window.
Note: You must use commas for this purpose, and full stops (.) for decimal numbers, and never use any thousands separators, regardless of your desired language.
Expressions
Keyboard Maestro’s expressions include precedence, nested bracketed expressions, many built-in functions, various numeric bases, so you should be able to write almost any expressions you might like to use, as well as use it as a general purpose calculator if desired.
Operators
Operators based on precedence from lowest to highest are:
Array Separator (,) – this is NOT an operator IMO. – this is NOT an operator IMO. | Allows a text Variable, which has comma separated values, to work somewhat like an Array. Assume MyKMVariable contains “value1,value2,value3”.Then MyKMVariable[2] returns “value2”. |
Ternary Operator (?) | a=b ? 3 : 4 |
Bitwise OR (|), Bitwise AND (&) and Bitwise XOR | operators |
Comparison Operators (<, ≤, =, >, ≥, ≠) | compare for (in)equality and return 0 or 1 |
Shift Operators (≪, ≫) | shift a number left or right |
| Arithmetic Operators • Add ( +)• Subtract ( -)• Multiply ( *)• Divide ( /) | A mathematical function that takes two operands and performs a calculation on them. |
Modulo (i MOD n) | The remainder of the division of i by n.Both values ( i, n) must be an integer in Keyboard Maestro. |
Power Operator (^) | exponentiation |
Unary Prefix Operators (√, -, ( ) ) | square root, negation, sub-expressions |
functions – While technically Functions are operators, it confusing to most users to list here since everywhere else in KM they are separated. – While technically Functions are operators, it confusing to most users to list here since everywhere else in KM they are separated. | a large variety of functions |
Numbers and Variables or Array Accesses (5,$5A,0x50,8#007,Variable,Variable[5]) – this is clear as mud. – this is clear as mud. | identifiers and values |
Unary Postfix Operators (!,%,°)) | factorial, percent, degrees |
You can use either = or == (v8+) for testing for equality.
Operators and functions must be in uppercase to minimize conflict with variables.
Functions
The available functions are listed on the wiki Functions page.
You can insert a function by name by choosing Insert Function by Name from the Edit menu.
Variables
In numeric calculation fields, Variable Names are used without the % that are used in text token fields. Do not try to use tokens (like %Variable%MyVar%) in numeric calculation fields, just use MyVar by itself. The variable must contain a valid numeric value, or an expression (v8+) that evaluates to a valid numeric value. So for example, if MyVar contains a text value of 2*3, then the calculation 4*MyVar will return 24.
Screen Coordinates
Keyboard Maestro refers to screen coordinates as two or four comma separated numbers in the text of a Keyboard Maestro Variable (which is always a string).
- Screen object points, like the left,top position of a window, have two values, like 12,34
- Screen object rectangles, like the frame of a window, have four values 12,34,56,78 (with a fifth value for fuzz in some instances).
* You can reference these values by position in the string, as it the Variable were an array: - For example:
if the VariablemyWindowis “12,34,56,78”
then all of these forms of reference will provide a value of 34 in a Calculation field:- myWindow[2]
- myWindow.y
- myWindow.Top
Variable Array Access
If a variable contains a sequence of numbers separated by comma (,) then you can access that variable using array notation (eg MyVar[5]). So if variable MyVar has a text value of 10,20,30,40,50,60, MyVar[5] will return 50.
The index is itself an expression, so it can be arbitrarily complex.
Indices are 1-based, so MyVar[1] is the first element. If the index is 0, the size of the array is returned (so MyVar[0] would be 6). If the index is less than zero, the array is indexed from the end (so MyVar[-5] would be 20).
Variable Dot Notation
In a Calculation field you can reference the numbers in a Keyboard Maestro Variable (which is always a string) using dot notation:
| Variable.x | x coordinate |
| Variable.y | y coordinate |
| Variable.left | the left coordinate of a rectangle |
| Variable.top | the top coordinate of a rectangle |
| Variable.right | the right coordinate of a rectangle |
| Variable.bottom | the right coordinate of a rectangle |
| Variable.width | the width of a rectangle or size |
| Variable.height | the height of a rectangle or size |
| Variable.fuzz | the fuzz of an image match (rectangle,fuzz) |
| Variable.MidX | the horizontal middle of a rectangle |
| Variable.MidY | the vertical middle of a rectangle |
The Variable Name and Dot reference are case insensitive.
Text Fields
In calculation fields, you can express a calculation as you would normally write an expression, for example:
3 * Count + 7
However in a text field, since any text is allowed, you must use percent encoded tokens to indicate where more processing is required. You can include a variable in the text by using the %Variable% token, or you can use a calculation by using the %Calculate% token, or any number of other Tokens.
The result is %Calculate%3 * Count + 7%.
Examples of Variable Data Reference
Macro Actions
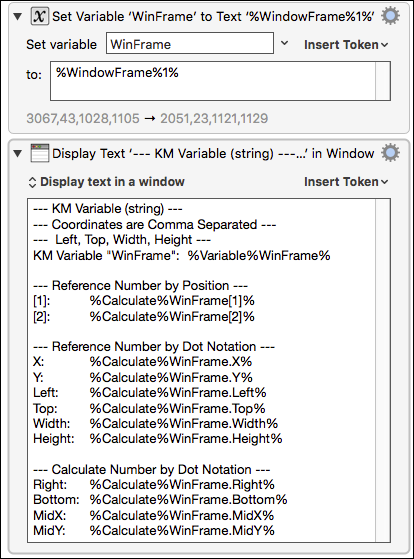
Example Results
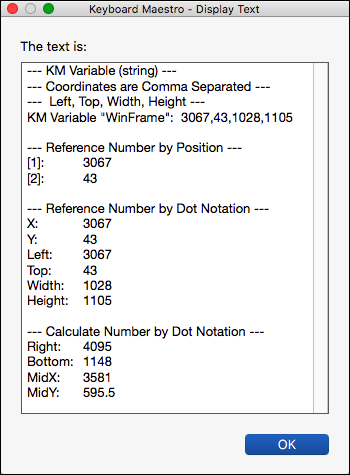
Some example expressions might be:
Amount in Dollars * 100 MJD() > 55928 NOW() > TIME(2012,3,23,12,2,1) DOW(TIME(2012,4,4)) = 4 Radius*SIN(20°),Radius*COS(20°) Window Frame[1]+Window Frame[3]/2,Window Frame.MidY MOUSEBUTTON() + 2 * MOUSEBUTTON(4) SCREEN(Internal,Left,10%)
KeyWords: MOD, Modulo
